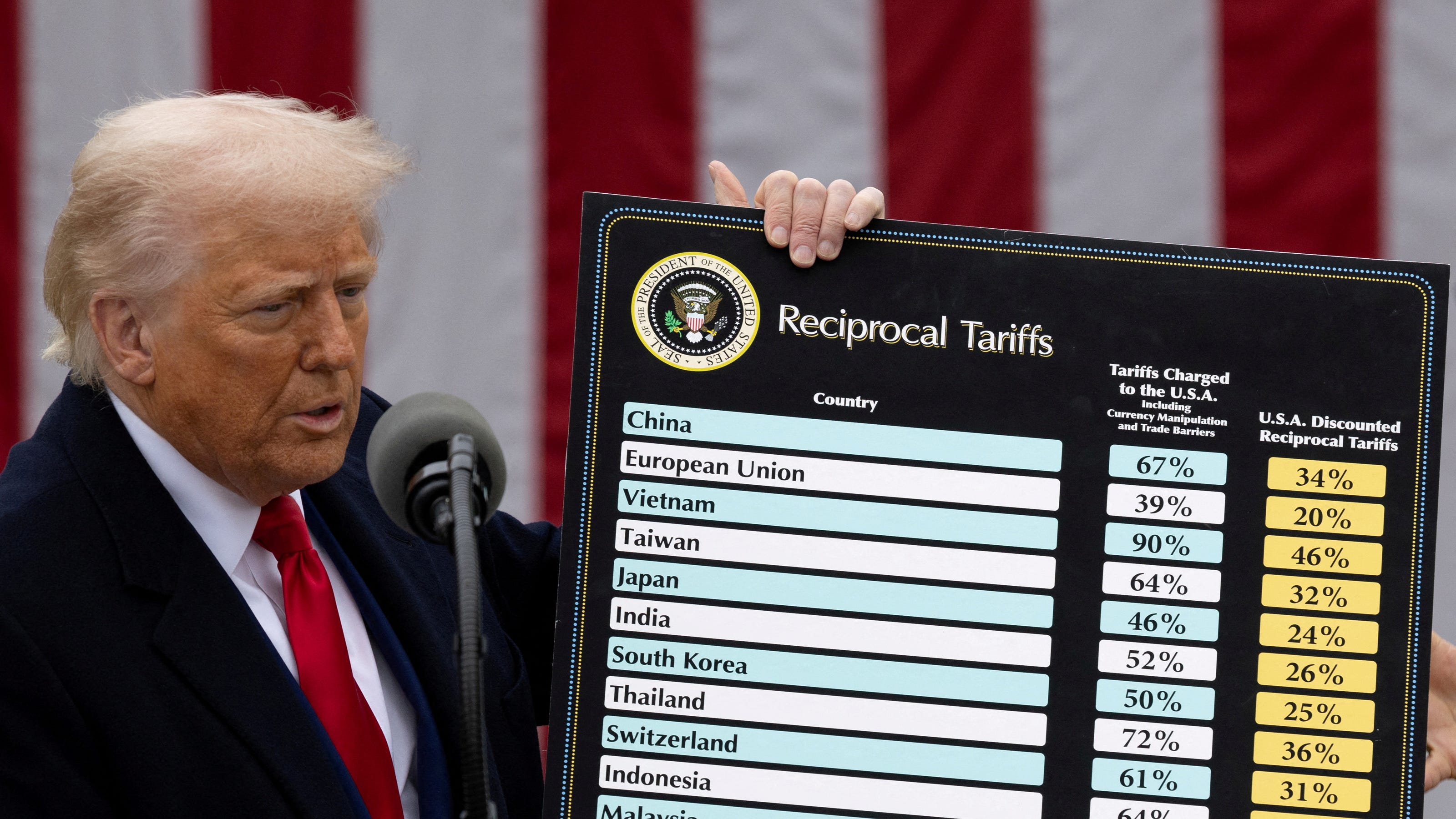
US Imposes Trump-Era 10% Tariff: Ripple Effects Across Industries
Editor’s Note: The reinstatement of a 10% tariff on certain goods imported from various countries, a policy initially enacted during the Trump administration, has taken effect today. This article analyzes the potential impact across key sectors.
Why This Matters: Understanding the Economic Ramifications of Renewed Tariffs
The reintroduction of the 10% tariff on goods imported from [list specific countries/regions affected] represents a significant development with far-reaching economic consequences. This policy shift impacts not only businesses directly involved in import/export but also consumers through potential price increases and supply chain disruptions. This article will explore the key sectors affected, analyze the potential economic consequences, and examine the potential for long-term implications on international trade relations. We will also address the broader political context surrounding this decision.
Key Takeaways
| Sector | Impact | Potential Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Goods | Increased prices, reduced consumer purchasing power | Increased domestic production, government subsidies |
| Manufacturing | Higher input costs, reduced competitiveness | Automation, diversification of supply chains |
| Agriculture | Fluctuations in agricultural commodity prices | Government support programs, diversification of export markets |
| Retail | Increased prices, potential for reduced sales | Price adjustments, inventory management |
| Small Businesses | Increased operating costs, potential for reduced profitability | Government assistance programs, cost-cutting measures |
US Imposes Trump's 10% Tariff: A Detailed Analysis
Introduction: The Return of a Controversial Policy
The reinstatement of the 10% tariff, a hallmark policy of the Trump administration, has reignited debates about protectionism versus free trade. This decision arrives at a time when [mention current economic climate – e.g., global inflation, supply chain challenges]. Understanding the implications of this policy requires examining its impact across different economic sectors.
Key Aspects of the Renewed Tariff
- Affected Goods: The tariff specifically targets [list the specific types of goods affected, with examples, e.g., steel, aluminum, certain consumer electronics].
- Origin Countries: The policy impacts imports from [list the countries affected].
- Implementation Details: [Explain the specific implementation details of the tariff – e.g., effective date, exemptions, etc.]
Detailed Analysis of Sectoral Impacts
The impact of the reinstated tariff will vary across industries. For example, the manufacturing sector may face higher input costs, potentially leading to reduced production and job losses. The consumer goods sector is likely to see price increases, which could negatively impact consumer spending. The agricultural sector might experience fluctuations in export markets and prices. Small businesses, already facing challenges, will likely bear a disproportionate burden. We will examine each sector in greater detail in subsequent sections.
Interactive Elements
The Impact on Consumer Prices
Introduction: Understanding how the 10% tariff translates into higher prices for consumers is crucial.
Facets:
- Price Increases: We expect to see a price increase of approximately [percentage] on [list specific goods].
- Consumer Response: Consumers may respond by reducing their purchases, switching to substitutes, or seeking out cheaper alternatives.
- Retailer Strategies: Retailers may absorb some of the increased costs or pass them fully onto consumers.
- Government Intervention: The government may take steps to mitigate the impact on consumers, such as providing subsidies or tax breaks.
Summary: The price impact is likely to be felt most strongly by lower-income consumers, who may face a significant reduction in purchasing power.
The Role of Supply Chains in Tariff Impact
Introduction: Global supply chains are already under stress. The renewed tariff adds another layer of complexity.
Further Analysis: The tariff could lead to increased reliance on domestic suppliers, but this may not be immediately feasible due to capacity constraints. Diversification of supply chains, although costly, is a potential mitigation strategy.
Closing: Managing supply chain disruptions and building resilience are crucial for mitigating the negative consequences of this policy.
People Also Ask (NLP-Friendly Answers)
Q1: What is the 10% tariff?
A: The 10% tariff is a tax imposed on certain imported goods from specific countries, increasing their price in the US market.
Q2: Why is this tariff important?
A: This tariff is significant due to its potential impact on inflation, consumer spending, international trade relations, and various economic sectors.
Q3: How can this tariff benefit me?
A: If you're a domestic producer competing with imported goods, the tariff might offer some protection. However, for most consumers, it likely leads to higher prices.
Q4: What are the main challenges with this tariff?
A: Challenges include higher prices for consumers, potential trade wars, and negative impacts on businesses relying on imported goods.
Q5: How to get started with understanding the tariff’s impact?
A: Stay informed about government announcements, analyze market trends for affected goods, and follow reports from economic experts.
Practical Tips for Navigating the Tariff's Impact
Introduction: Businesses and consumers need to adapt to the changing economic landscape.
Tips:
- Diversify supply chains: Reduce reliance on single sources of imported goods.
- Negotiate with suppliers: Seek better pricing terms.
- Monitor market trends: Stay informed about price changes and consumer demand.
- Explore cost-cutting measures: Find ways to reduce operating expenses.
- Seek government assistance: Look for programs designed to help businesses and consumers impacted by tariffs.
- Consider alternative products: Explore substitutes for affected imported goods.
- Invest in domestic production: Support local manufacturers whenever possible.
- Engage in advocacy: Participate in discussions about trade policy.
Summary: Proactive measures are key to mitigating the negative consequences of the tariff.
Transition: Understanding the broader implications of the 10% tariff requires a look at the bigger picture.
Summary (Resumen)
The reintroduction of the 10% tariff on certain imported goods carries significant implications for the US economy. This policy shift will affect various sectors, leading to potential price increases, supply chain disruptions, and impacts on consumer purchasing power. Businesses and consumers need to adapt proactively to navigate these challenges.
Closing Message (Mensaje Final)
The economic ramifications of the reinstated tariff will unfold over time. The coming months will be crucial for observing its impact on prices, employment, and international trade relations. What strategies will prove most effective for navigating this uncertain economic landscape?
Call to Action (Llamada a la Acción)
Stay informed on the latest developments by subscribing to our newsletter, and share this article to help others understand the potential impacts of this policy.
(Hreflang tags would be inserted here, specifying language and region variations of the article)